An Introduction to Windows Communication Foundation (WCF)
WCF Overview
1.0 What Is WCF?
WCF stands for Windows Communication Foundations.
WCF combines the functionality from ASP.NET Web Services, .NET Remoting, Message Queuing and Enterprise Services.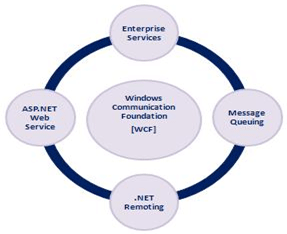
WCF provides the following features,
- Hosting For Component & Services
WCF Service can be hosted in ASP.NET Runtime, a Windows Service, a COM+ Component or just a Windows form application for peer-to-peer computing. - Declarative Behavior
Similar to ASP.NET Web Services, attributes can be used for WCF Services e.g. ServiceContract(), OperationContract, DataContract and DataMember - Communication Channels
Similar to .NET Remoting WCF Services are flexible in changing the channels. WCF offers multiple channels to communicate using HTTP, TCP or an IPC channel. - Security
- Extensibility
2.0 Understanding WCF-
These days we are creating the software/application which should be capable of communication with other applications as well. Communication with other application simply means either sharing/exchanging the data or the sharing the logic.
Now, this communication may be of two kinds
- Over Intranet (Same Network/Platform i.e. .NET Application to .NET Application)
- Over Internet (Cross Platform may be ASP.NET to J2EE Application)
Suppose we are writing a .NET Software with n-tier architecture in which Win Form Client needs to communicate with Server in the same network. In such case we may go for .NET Remoting for communication between Client and Server.
Suppose, once our software mentioned above is ready, we need to expose some business logic to another J2EE application. This J2EE application is supposed to use our .NET Application's logic over WWW. In such case we will have to write new ASP.NET Web Service to expose the logic.
Picture shown below shows the limitation of .NET Remoting

Comments